Lysosome passivation triggered by silver nanoparticles enhances subcellular-targeted drug therapy†
Abstract
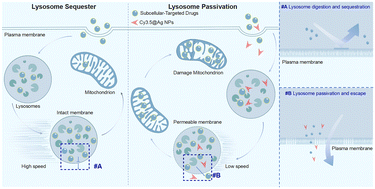
Frequently, subcellular-targeted drugs tend to accumulate in lysosomes after cellular absorption, a process termed the lysosomal trap. This accumulation often interferes with the drug's ability to bind to its target, resulting in decreased efficiency. Existing methods for addressing lysosome-induced drug resistance mainly involve improving the structures of small molecules or enveloping drugs in nanomaterials. Nonetheless, these approaches can lead to changes in the drug structure or potentially trigger unexpected reactions within organisms. To address these issues, we introduced a strategy that involves inactivating the lysosome with the use of Ag nanoparticles (Cy3.5@Ag NPs). In this method, the Cy3.5@Ag NPs gradually accumulate inside lysosomes, leading to permeation of the lysosomal membrane and subsequent lysosomal inactivation. In addition, Cy3.5@Ag NPs also significantly affected the motility of lysosomes and induced the occurrence of lysosome passivation. Importantly, coincubating Cy3.5@Ag NPs with various subcellular-targeted drugs was found to significantly increase the efficiency of these treatments. Our strategy illustrates the potential of using lysosomal inactivation to enhance drug efficacy, providing a promising therapeutic strategy for cancer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...