Photophysicochemical and electrochemical properties of pyrene–BODIPY platforms†
Abstract
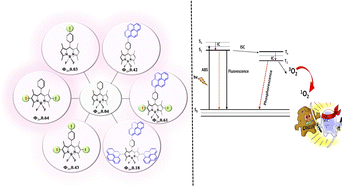
The photochemical, photophysical, and electrochemical properties of BODIPY compounds (1–7) substituted with iodine or pyrene at the 2-, 6-, or 8-positions (meso) were thoroughly investigated in this study. Through the incorporation of iodine and/or pyrene moieties into the BODIPY derivatives, we evaluated their impact on the photophysical properties using both steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence analyses. Notably, the heavy atom effect induced by iodine was observed, leading to an increase in singlet oxygen quantum yield in proportion to fluorescence intensity. Furthermore, the introduction of pyrene at the meso position in BODIPY (compound 5) significantly enhanced the π-conjugated system and facilitated the generation of singlet oxygen. Intriguingly, compound 7, which featured pyrene substitutions at positions 2, 6, and 8, exhibited a reduced singlet oxygen yield when compared to the iodine-substituted compound 6. Moreover, we conducted an evaluation of the electrochemical properties of the BODIPY compounds (1–7) in dichloromethane. Additionally, we characterized the structures of the synthesized compounds (5♦, 6, and 7) using various spectroscopic techniques, including FT-IR, HRMS, and NMR (1H, 13C, 19F, and 11B), which were performed for the first time within the scope of this study. The comprehensive findings obtained from this extensive research contribute valuable knowledge that has the potential to guide the development of highly efficacious photosensitizers for applications in photodynamic therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...