Interaction of phytate with cyclic polyamines†
Abstract
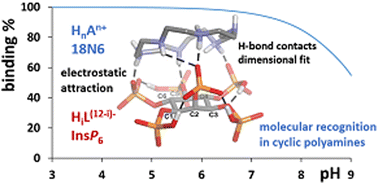
myo-Inositol hexakisphosphate (InsP6) is a widespread molecule, present in relatively high concentrations in nature, and plays key roles in many metabolic processes. Its complex chemistry arises from the presence of flexible ring bearing six multivalent phosphates that can either be anionic or interact with a myriad of cationic species in solution, including protonated polyamines. Understanding the interaction of this biomolecule with inorganic and organic cations aims to gain a better picture of its chemical and structural behavior in biological systems. Building on our previous work on the interaction of InsP6 with inorganic cations and linear polyamines, here, in this study, we present the corresponding interaction with cyclic polyamines via potentiometry, with the help of computational tools, in order to understand the main determinants of the stability of the formed species and the structural insights that rationalize the interaction. Stable InsP6 : polyamine 1 : 1 species are detected and the strength of the interaction results from an interplay of electrostatic attractions and hydrogen bonding formation. Even though the results show a certain resemblance to the interaction of InsP6 with linear polyamines, the higher rigidity imposed by cyclization increases the selectivity of InsP6 towards polyamines, giving rise to the molecular recognition of hexamine 18N6, due to the spatial geometric fit of the charge distribution of the interacting anionic InsP6 and the protonated polyamine.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...