Ferromagnetic “nickel core–cobalt shell” catalysts for NaBH4 hydrolysis
Abstract
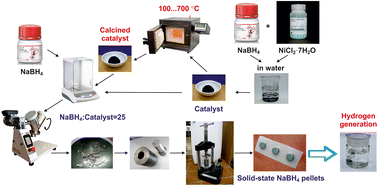
Nickel catalysts were synthesized for solid-state NaBH4 composites by reducing nickel chloride with sodium borohydride. The effect of heat treatment on their magnetic properties and the hydrogen generation rate was studied. It has been established that calcination of nickel catalysts to 350 °C has a negligible effect on the rate of gas generation but provides fast separation of more than 70% of the catalyst from the spent reaction medium using a magnet. According to XRD data (in situ) and the found Curie point value (358 °C), the enhancement of magnetic properties results from the accumulation of the ferromagnetic phase of the reduced Ni0 metal. A further increase in the heat treatment temperature (≥400 °C) decreases the activity of nickel catalysts, accompanied by a decrease in the specific surface area of the samples, by the complete conversion of cobalt boride Ni3B into the metallic form Ni0 and by the formation of the boron oxide shell around the nickel particles. To increase the activity of the nickel catalyst calcined at 350 °C, cobalt was deposited using incipient wetness impregnation, followed by reduction with sodium borohydride. The proposed technique allowed us to uniformly anchor cobalt on the surface of nickel particles, which ensured an increase in the gas generation rate. Thus, an effective ferromagnetic cobalt–nickel catalyst has been proposed for solid-state hydrogen-generating materials based on sodium borohydride. Note that the removal extent of this catalyst from the spent solution was about 85%.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...