Hepatoprotective efficacy and interventional mechanism of the panaxadiol saponin component in high-fat diet-induced NAFLD mice
Abstract
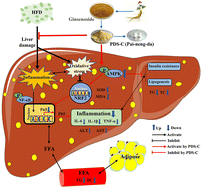
Dietary administration is a promising strategy for intervention in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Our research team has identified a biologically active component, the panaxadiol saponin component (PDS-C) isolated from total saponins of panax ginseng, which has various pharmacological and therapeutic functions. However, the efficacy and mechanism of PDS-C in NAFLD were unclear. This study aimed to elucidate the hepatoprotective effects and underlying action mechanism of PDS-C in NAFLD. Mice were fed a high-fat diet (HFD) for 8 weeks to induce NAFLD and treated with PDS-C and metformin as the positive control for 12 weeks. PDS-C significantly alleviated liver function, hepatic steatosis and blood lipid levels, reduced oxidative stress and inflammation in NAFLD mice. In vitro, PDS-C has been shown to reduce lipotoxicity and ROS levels while enhancing the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capabilities in HepG2 cells induced by palmitic acid. PDS-C induced AMPK phosphorylation, leading to upregulation of the Nrf2/HO1 pathway expression and downregulation of the NFκB protein level. Furthermore, our observations indicate that PDS-C supplementation improves insulin resistance and glucose homeostasis in NAFLD mice, although its efficacy is not as pronounced as metformin. In conclusion, these results demonstrate the hepatoprotective efficacy of PDS-C in NAFLD and provide potential opportunities for developing functional products containing PDS-C.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...