Sustainable remediation of paint factory wastewater using electrocoagulation†
Abstract
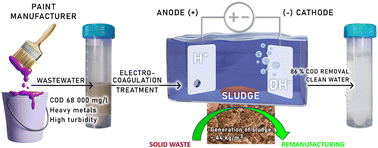
The electrochemical treatment of wastewater from paint factories offers a promising solution for the intricate mix of pollutants present in the effluent. This paper investigates applying the electrocoagulation (EC) technique to treat wastewater from a specific paint factory in Slovakia, emphasizing its potential advantages in capturing solid sludge for potential remanufacturing and addressing implementation challenges. The EC method has proven highly efficient in reducing key parameters like chemical oxygen demand (∼86%), turbidity, and concentrations of toxic compounds, including phosphorus and heavy metals, in paint factory wastewater (PFW). Notably, the EC process generates valuable sludge as a recyclable material. Through meticulous analysis using scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, the sludge's potential for diverse industrial applications is explored. Emphasizing the principles of a circular economy, repurposing these materials contributes to environmental sustainability, reducing waste disposal and the need for new resources. This study highlights the successful implementation of EC to achieve ecological remediation and sustainability goals in the paint industry, and through detailed material analysis, it also reveals the potential of sludge for remanufacturing purposes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...