In situ sonochemical synthesis of flower-like N-graphyne/BiOCl0.5Br0.5 microspheres for efficient removal of levofloxacin
Abstract
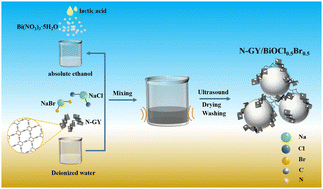
In this work, N-graphyne is in situ coupled with BiOCl0.5Br0.5via a facile one-step sonochemical method. To our knowledge, both the synthesis strategy for BiOCl0.5Br0.5 and the N-graphyne/BiOCl0.5Br0.5 photocatalytic system are new developments. A collection of characterization methods is adopted to detect the morphologies, structures, and electronic and optical properties. The results demonstrate that wrinkle-like N-graphyne nanosheets successfully enwind around or on flower-like BiOCl0.5Br0.5 microspheres, which are regularly assembled by BiOCl0.5Br0.5 nanosheets. Compared with pristine BiOCl0.5Br0.5, N-graphyne/BiOCl0.5Br0.5 composites exhibit superior adsorption capacity and visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of levofloxacin. In particular, the optimal N-graphyne amount for ameliorating the photocatalytic performance of BiOCl0.5Br0.5 is ascertained. In addition, the good stable performance for photocatalysis is confirmed by four cycling experiments. The dominant active species is confirmed to be O2˙− during photodegradation. The improved photocatalytic activity is attributed to the enhanced visible light response and the accelerated transfer/separation of photogenerated carriers by N-graphyne, which are verified using UV–vis absorption spectra, photocurrents, photopotentials, Nyquist plots, and Mott–Schottky curves. This study develops a new perspective for the synthesis and modification of BiOX solid solution, which can be used as an efficient photocatalyst.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...