A theoretical study of the mechanism of cationic polymerization of isobutylene catalysed by EtAlCl2/t-BuCl with bis(2-chloroethyl)ether in hexanes†
Abstract
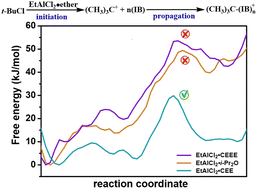
The mechanism of cationic polymerization of isobutylene catalyzed by t-BuCl/ethylaluminum dichloride (EADC) combined with bis(2-chloroethyl)ether (CEE) in n-hexane solvent has been investigated using ab initio molecular dynamics (AIMD) and metadynamics (MTD) simulations. The results indicated that the polyisobutylene (PIB) initiation stage involves a clear two-step mechanism. Calculation of the free energy landscapes of the other two ether reactions reveals that the energy barriers of diisopropyl ether (i-Pr2O) and 2-chloroethyl ethyl ether (CEEE) are much higher than those of CEE, which is consistent with the experimental results. During the chain propagation phase, the required free energy barrier gradually decreases and tends to reach equilibrium as the chain length increases. Finally, the oxonium mechanism during the chain initiation stage was investigated by calculating the 1H NMR spectra and MTD simulation. Our calculations can confirm that the existence of tert-butyloxonium ions during the reaction is possible. Their contribution to the whole reaction is further discussed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...