Anti-proliferative, -migratory and -clonogenic effects of long-lasting nitric oxide release in HepG2 cells†
Abstract
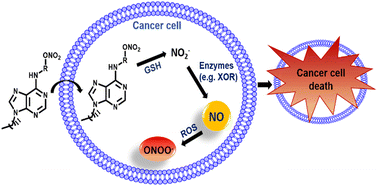
Nitric oxide (NO) holds promise as a cytotoxic agent against tumors, but its gaseous nature and short half-life hinder direct administration to tumor tissues. Herein, we present novel 6,9-disubstituted purine derivatives designed to ensure sustained NO release, followed by study of their significant anti-proliferative, anti-migratory, and anti-clonogenic effects on HepG2 cell lines, highlighting NO release as a potent effector for treating hepatocellular carcinoma.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...