Copper(ii)-based metal–organic framework delivery of calcium ascorbate for enhanced chemodynamic therapy via H2O2 self-supply and glutathione depletion†
Abstract
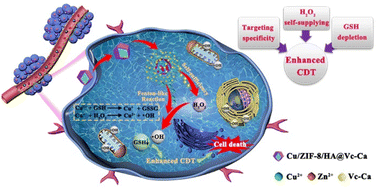
Chemodynamic therapy (CDT) is a promising cancer treatment strategy. However, mild acidic pH, insufficient H2O2 content, and overexpressed glutathione (GSH) in the tumor microenvironment (TME) severely impair CDT efficiency. In this study, a novel therapeutic nanosystem (Cu/ZIF-8/Vc-Ca/HA) was constructed for H2O2 self-supply and GSH depletion co-enhanced CDT. Typically, calcium ascorbate (Vc-Ca) loaded on the surface of Cu2+-doped ZIF-8 (Cu/ZIF-8) was designed as an original source for H2O2 generation, and a hyaluronic acid (HA) shell was subsequently coated to act as a tumor-targeted “guide” and protective layer. Along with the HA shell disintegrated in the TME, exposed Cu/ZIF-8/Vc-Ca dissociated in the tumor acidic microenvironment, thus triggering the release of Vc-Ca and Cu2+. Vc-Ca selectively produced H2O2 in tumor cells, which provided abundant H2O2 for boosting Fenton-like reactions. Meanwhile, the released Cu2+ could get converted into Cu+ by consuming excess intracellular GSH, which could reduce the tumor antioxidant capability of the nanosystem. Moreover, byproduct Cu+ reacted with abundant H2O2 by a highly efficient Fenton-like reaction to generate toxic ˙OH. Biological assays indicated that the Cu/ZIF-8/HA@Vc-Ca nanosystem showed significant anticancer activity by enhancing the CDT process. This study may provide a new strategy for improving the effectiveness of CDT.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...