Silk-based organic photoresists for extreme ultraviolet lithography: a multiscale in silico study†
Abstract
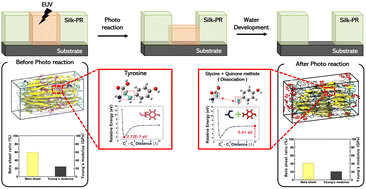
The development of photoresists (PRs) for extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography has become increasingly popular in the field of semiconductor nanopatterning. However, the rinsing process during sub-10 nm nanopatterning can severely impact the structural integrity of the existing PR materials; therefore, novel, robust PR materials are required. Here, we propose silk procured from silkworms as a potential PR for EUV lithography applications owing to its organic, biocompatible, and ecofriendly nature, and also its excellent mechanical properties. Its structural stability was examined using multiscale in silico methods, and its photoreactivity was evaluated via quantum mechanical calculations, and molecular dynamics simulations were performed to observe the silk peptide assembly behavior after EUV lithography. Moreover, an elastic network model was constructed, and normal mode analysis was conducted to approximate the mechanical properties of the assembled silk peptides. The data demonstrate how photoionization cleaved the covalent bonds between the Cα–Cβ atoms within tyrosine, which eventually destabilized the assembled silk peptides. In addition, the collapse of the secondary structure of the silk peptides after EUV lithography treatment indicated the instability of the self-assembled structure. Nevertheless, despite its organic nature, the photoionized silk exhibited a 25% increase in its Young's modulus compared with those of other PRs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...