Synthesis of biologically derived poly(pyrogallol) nanofibers for antibacterial applications†
Abstract
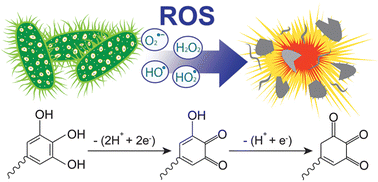
Herein, we present the facile synthesis of poly(pyrogallol) biopolymers and their application as antibacterial agents. Pyrogallol is a class of phenolic compounds that can be found in various plants. Polymerization was performed by the auto-oxidation of pyrogallol under a hydrated condition. The microscopic image of poly(pyrogallol) shows a highly homogenous nanofibrous structure with a diameter of 100.3 ± 16.3 nm. Spectroscopic analysis by FT-IR spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and XPS corroborated the formation of ether (C–O–C) bonds between the hydroxyl group and adjacent carbons of pyrogallol during polymerization. The FT-IR and XPS spectra also revealed redox-active gallol functional groups on poly(pyrogallol) nanofibers, which can be used to release free electrons and protons during oxidation followed by the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). The generated ROS from poly(pyrogallol) was used to inhibit the growth of bacteria, Escherichia coli, at a inhibition rates of 56.3 ± 9.7% and 95.5 ± 2.0% within 0.5 and 2 h, respectively. This finding suggests that poly(pyrogallol) can be used as a naturally occurring antibacterial agent for various biomedical and environmental applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...