Dicarboxylate-containing and fully substituted ferrocene with rapid dissolvability, high solubility, good stability, and moderate formal potential for mediated electrochemical detection†
Abstract
An electron mediator with rapid dissolvability and high solubility in aqueous electrolyte solutions is essential for point-of-care testing based on mediated electrochemical detection. However, most ferrocenyl (Fc) compounds have slow dissolvability and poor solubility owing to high hydrophobicity of the Fc backbone. Moreover, many Fc compounds have poor stability and nonoptimal formal potential (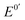 ). Herein, we present an Fc compound, Fc8m2c, which exhibits rapid dissolvability, high solubility, good stability, and moderate
). Herein, we present an Fc compound, Fc8m2c, which exhibits rapid dissolvability, high solubility, good stability, and moderate 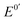 along with its high electron-mediation rate. The
along with its high electron-mediation rate. The 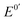 of Fc8m2c (0.17 V vs. Ag/AgCl) is tuned by two electron-withdrawing acyl substituents and eight electron-donating methyl substituents. Two pendant carboxylate groups of Fc8m2c allow for rapid dissolvability and high solubility (0.63 M in water), whereas full substitution in its two cyclopentadienyl ligands facilitates good chemical stability against decomposition in the presence of dissolved O2 and ambient light. A moderate
of Fc8m2c (0.17 V vs. Ag/AgCl) is tuned by two electron-withdrawing acyl substituents and eight electron-donating methyl substituents. Two pendant carboxylate groups of Fc8m2c allow for rapid dissolvability and high solubility (0.63 M in water), whereas full substitution in its two cyclopentadienyl ligands facilitates good chemical stability against decomposition in the presence of dissolved O2 and ambient light. A moderate 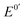 enables the application of a potential of 0.07 V at which electrochemical background currents are low and also contributes toward resisting the decomposition of both Fc8m2c and Fc8m2c+. Fc8m2c provides a high electron-mediation rate constant (2.4 × 106 M−1 s−1) in glucose detection using glucose dehydrogenase. When Fc8m2c is applied to a glucose sensor, the calculated detection limit is ∼0.1 mM with a measurement period of 5 s. Considering that the normal concentration of glucose in serum is between 3.9 and 6.6 mM, the detection limit is sufficiently low. These results show that Fc8m2c is an excellent electron-mediator candidate for sensitive and rapid glucose detection.
enables the application of a potential of 0.07 V at which electrochemical background currents are low and also contributes toward resisting the decomposition of both Fc8m2c and Fc8m2c+. Fc8m2c provides a high electron-mediation rate constant (2.4 × 106 M−1 s−1) in glucose detection using glucose dehydrogenase. When Fc8m2c is applied to a glucose sensor, the calculated detection limit is ∼0.1 mM with a measurement period of 5 s. Considering that the normal concentration of glucose in serum is between 3.9 and 6.6 mM, the detection limit is sufficiently low. These results show that Fc8m2c is an excellent electron-mediator candidate for sensitive and rapid glucose detection.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...