Chemically induced crosslinked enhanced emission of carbon polymer dots discerning healthy and cancer cells through pH-dependent tunable photoluminescence†
Abstract
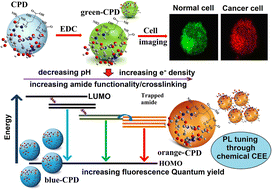
Chemically induced crosslinked enhanced emission (CEE) of urea and citric acid-derived carbon polymer dot (CPD) nanoparticles is established here with a rare zero linker approach, i.e. without the use of any separate crosslinkers. Such chemical CEE like any chemical reaction was achieved through amide bond formation using carbodiimide chemistry, pointing towards the feasibility of developing a general methodology for their formation through engineering the nanoparticle surface functionality. Exhaustive characterization was done to pinpoint the structure, morphology, and photophysics of the CPDs and concurrently eliminate the possibility of the involvement and interference by molecular fluorophores for the unique optical tuning of the CPDs. The structure–photophysics relation was further restated through theoretical studies involving density functional theory (DFT) that correlated significantly well with the experimental findings. Most interestingly, the CPDs revealed pH responsiveness due to the formation or hydrolysis of amide bonds with acid or base, respectively, which was manifested through a spectacular change in fluorescence emission visible to the naked eye through UV illumination. This distinct pH-dependent photoluminescence properties of CPDs opens up an enormous opportunity for interesting applications, including discriminating normal and cancerous cells, which we demonstrate herein as a proof of concept through in vitro imaging.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...