A novel stable zinc–oxo cluster for advanced lithography patterning†
Abstract
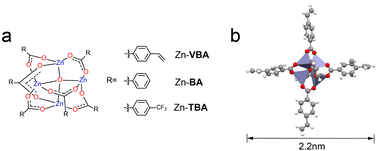
Recently, the development of novel metal-containing resists has received much attention in extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUVL) owing to their smaller sizes and higher EUV absorptivity than traditional polymer resists. Herein, we report zinc (Zn)–VBA, a novel stable zinc–oxo cluster-based photoresist molecule with the [Zn4O]6+ inner core and six organic ligands based on 4-vinylbenzoic acid. Zn–VBA was simply prepared by the reactions between the zinc-oxide and 4-vinylbenzoic acid, exhibiting atomically precise structure and good batch stability. Based on single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis, the size of Zn–VBA is 2.2 nm, which is in line with the high-resolution requirements for advanced lithography technology. Zn–VBA exhibits excellent thermal stability up to 400 °C, much better than the reported zinc-based clusters. Moreover, theoretical studies have revealed the roles of organic ligands in their high thermal stability. Spin-coating methods were employed to fabricate homogenous thin films of Zn–VBA, which showed a quite small roughness value in the absence of viscosifiers, as confirmed by atomic force microscopy images. More importantly, the Zn–VBA films performed well in the electron beam lithography (EBL) and EUVL tests without the addition of photoinitiators, giving prominent pattern lines. This work proves the structural advantages of benzoic-acid-based zinc–oxo clusters as promising EUV patterning materials, which inspire future exploration of metal–oxo clusters (MOCs) resist materials for advanced lithography.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Photofunctional Materials and Transformations


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...