Multiconfigurational photodynamics simulations reveal the mechanism of photodecarbonylations of cyclopropenones in explicit aqueous environments†
Abstract
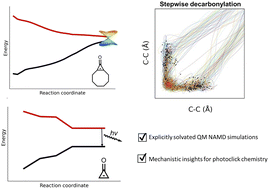
Gas-evolving photochemical reactions use light and mild conditions to access strained organic compounds irreversibly. Cyclopropenones are a class of light-responsive molecules used in bioorthogonal photoclick reactions; their excited-state decarbonylation reaction mechanisms are misunderstood due to their ultrafast (<100 femtosecond) lifetimes. We have combined multiconfigurational quantum mechanical (QM) calculations and non-adiabatic molecular dynamics (NAMD) simulations to uncover the excited-state mechanism of cyclopropenone and a photoprotected cyclooctyne-(COT)-precursor in gaseous and explicit aqueous environments. We explore the role of H-bonding with fully quantum mechanical explicitly solvated NAMD simulations for the decarbonylation reaction. The cyclopropenones pass through asynchronous conical intersections and have dynamically concerted photodecarbonylation mechanisms. The COT-precursor has a higher quantum yield of 55% than cyclopropenone (28%) because these trajectories prefer to break a σCC bond to avoid the strained trans-cyclooctene geometries. Our solvated simulations show an increased quantum yield (58%) for the systems studied here.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...