Isomerization-induced fluorescence enhancement of two new viologen derivatives: mechanism insight and DFT calculations†
Abstract
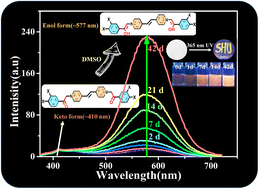
The dark-colored viologen radical cations are unstable in air and easily fade, thus greatly limiting their applications. If a suitable substituent is introduced into the structure, it will have the dual function of chromism and luminescence, which will broaden its application field. Here, Vio1·2Cl and Vio2·2Br were synthesized by introducing aromatic acetophenone and naphthophenone substituents into the viologen structure. The keto group (–CH2CO–) on the substituents is prone to isomerize into the enol structure (–CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) COH–) in organic solvents, especially in DMSO, resulting in a larger conjugated system to stabilize the molecular structure and enhance fluorescence. The time-dependent fluorescence spectrum shows obvious keto-to-enol isomerization-induced fluorescence enhancement. The quantum yield also increased significantly (T = 1 day, ΦVio1 = 25.81%, ΦVio2 = 41.44%; T = 7 days, ΦVio1 = 31.48%, and ΦVio2 = 54.40%) in DMSO. The NMR and ESI-MS data at different times further confirmed that the fluorescence enhancement was caused by isomerization, and no other fluorescent impurities were produced in solution. DFT calculations show that the enol form is almost coplanar throughout the molecular structure, which is conducive to stabilizing the structure and enhancing fluorescence. The fluorescence emission peaks of the keto and enol structures of Vio12+ and Vio22+ were at 416–417 nm and 563–582 nm, respectively. The fluorescence relative oscillator strength of Vio12+ and Vio22+ enol structures is significantly higher than that of keto structures (f value changes from 1.53 to 2.63 for Vio12+ and from 1.62 to 2.81 for Vio22+), indicating stronger fluorescence emission of the enol structure. The calculated results are in good agreement with the experimental results. Vio1·2Cl and Vio2·2Br are the first examples of isomerization-induced fluorescence enhancement of viologen derivatives, which shows strong solvatofluorochromism under UV light, making up for the disadvantage that it is easy for a viologen radical to fade in air, and providing a new strategy for designing and synthesizing viologen materials with strong fluorescence.
COH–) in organic solvents, especially in DMSO, resulting in a larger conjugated system to stabilize the molecular structure and enhance fluorescence. The time-dependent fluorescence spectrum shows obvious keto-to-enol isomerization-induced fluorescence enhancement. The quantum yield also increased significantly (T = 1 day, ΦVio1 = 25.81%, ΦVio2 = 41.44%; T = 7 days, ΦVio1 = 31.48%, and ΦVio2 = 54.40%) in DMSO. The NMR and ESI-MS data at different times further confirmed that the fluorescence enhancement was caused by isomerization, and no other fluorescent impurities were produced in solution. DFT calculations show that the enol form is almost coplanar throughout the molecular structure, which is conducive to stabilizing the structure and enhancing fluorescence. The fluorescence emission peaks of the keto and enol structures of Vio12+ and Vio22+ were at 416–417 nm and 563–582 nm, respectively. The fluorescence relative oscillator strength of Vio12+ and Vio22+ enol structures is significantly higher than that of keto structures (f value changes from 1.53 to 2.63 for Vio12+ and from 1.62 to 2.81 for Vio22+), indicating stronger fluorescence emission of the enol structure. The calculated results are in good agreement with the experimental results. Vio1·2Cl and Vio2·2Br are the first examples of isomerization-induced fluorescence enhancement of viologen derivatives, which shows strong solvatofluorochromism under UV light, making up for the disadvantage that it is easy for a viologen radical to fade in air, and providing a new strategy for designing and synthesizing viologen materials with strong fluorescence.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...