NiFe-LDH coated NiSe/Ni foam as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting†
Abstract
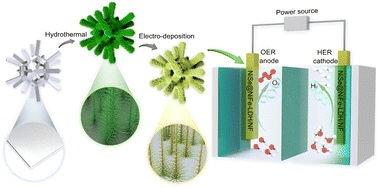
Electrocatalytic water splitting is promising for renewable hydrogen production, yet relies on the development of a highly active and stable electrocatalyst. Herein, we report the construction of a bifunctional heterostructure electrocatalyst in the form of NiFe layered double hydroxide coated NiSe/Ni foam (NiSe@NiFe-LDH/NF) for efficient electrocatalytic water splitting. Benefiting from the superior electrical conductivity and high specific surface area of NiSe, the high active site density of NiFe-LDH, the fast charge transfer rate at a tight interface, and the strong corrosion resistance of the shell layer, NiSe@NiFe-LDH/NF exhibited excellent electrocatalytic activity and stability towards the oxygen evolution reaction (209 mV@10 mA cm−2, 241 mV@100 mA cm−2), hydrogen evolution reaction (93 mV@10 mA cm−2, 213 mV@100 mA cm−2), and overall water splitting (1.560 V@10 mA cm−2) in 1 M KOH electrolyte. This work thus provides new insights into the design of more efficient and stable bifunctional non-noble metal electrocatalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...