Suitable commercial catalysts for the synthesis of oxymethylene dimethyl ethers†
Abstract
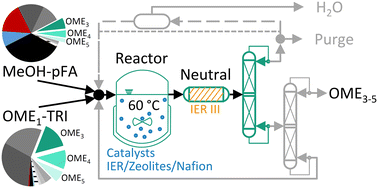
OME have diesel fuel like properties with almost soot-free combustion, which can enable a reduction of nitrogen oxides. This makes them promising candidates for internal combustion engines as blends or neat fuel. Moreover, OME are addressed as environmentally benign solvents and as hydrogen dense carriers for fuel cells. OME are produced from methanol which can be produced sustainably, allowing a significant overall reduction of CO2 emissions. Various catalysts have been investigated for OME synthesis focusing on selectivity and activity. This study concentrates on commercial heterogeneous catalysts and compares not only the conversions, selectivities and the target product yield but also the activity, side product formation and thermal stability of the synthesis products. Various ion exchange resins, zeolites and Nafion catalysts were applied for the OME synthesis in a batch autoclave at 60 °C for the aqueous reaction systems methanol/paraformaldehyde and the anhydrous reaction system OME1/trioxane. Investigations of the synthesis products in a micro distillation setup showed that all applied catalysts lead to active species in the synthesis product, negatively impacting its thermal stability. This indicates that a synthesis product handling step is necessary prior to the downstream purification. Based on these investigations, ion exchange resins are identified as the most suitable for industrial OME synthesis due to their higher activity and lower side product formation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...