Discovery of new pyridine heterocyclic hybrids; design, synthesis, dynamic simulations, and in vitro and in vivo breast cancer biological assays†
Abstract
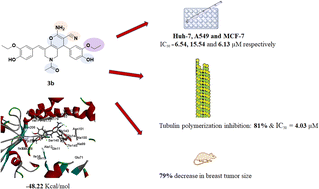
Pyridine is a nitrogen bearing heterocyclic scaffold that shows a wide range of biological activities. The pyridine nucleus has become an interesting target for medicinal chemistry researchers worldwide. Several pyridine derivatives exhibited good anticancer effects against diverse cell lines. Therefore, to explore new anticancer pyridine entities, novel pyridine derivatives were designed and synthesized and evaluated for their anticancer abilities in vitro and in vivo. All of the target compounds were evaluated against three different human cancer cell lines (Huh-7, A549 and MCF-7) via MTT assay. Most of the compounds exhibited significant cytotoxic activities. Compounds 3a, 3b, 5a and 5b showed superior antiproliferative activities to Taxol. Where, compound 3b showed IC50 values of 6.54, 15.54 and 6.13 μM compared to Taxol (6.68, 38.05, 12.32 μM) against Huh-7, A549 and MCF-7, respectively. Also, tubulin polymerization assay was carried out. The most potent compounds 3a, 3b, 5a and 5b could significantly inhibit tubulin polymerization with IC50 values of 15.6, 4.03, 6.06 and 12.61 μM, respectively. Compound 3b exhibited the highest tubulin polymerization inhibitory effect with an IC50 value of 4.03 μM compared to combretastatin (A-4) (1.64 μM). Molecular modeling studies of the designed compounds confirmed that most of the compounds made the essential binding interactions compared to the reference compound which assisted in the prediction of the structure requirements for the detected anticancer activity. Finally, in vivo studies showed that compound 3b could significantly inhibit breast cancer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...