The role of ethylene carbonate (EC) and tetramethylene sulfone (SL) in the dissolution of transition metals from lithium-ion cathodes†
Abstract
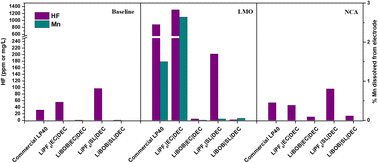
Transition metal (TM) dissolution is a direct consequence of cathode–electrolyte interaction, having implications not only for the loss of redox-active material from the cathode but also for the alteration of solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) composition and stability at the counter electrode. It has widely been reported that the limited anodic stability of typical carbonate-based electrolytes, specifically ethylene carbonate (EC)-based electrolytes, makes high-voltage cathode performance problematic. Hence, the more anodically stable tetramethylene sulfone (SL) has herein been utilized as a co-solvent and a substitute for EC in combination with diethyl carbonate (DEC) to investigate the TM dissolution behavior of LiN0.8C0.17Al0.03 (NCA) and LiMn2O4 (LMO). EC|DEC and SL|DEC solvents in combination with either LiPF6 or LiBOB salts have been evaluated, with LFP as a counter electrode to eliminate the influence of low potential anodes. Oxidative degradation of EC is shown to propagate HF generation, which is conversely reflected by an increased TM dissolution. Therefore, TM dissolution is accelerated by the acidification of the electrolyte. Although replacing EC with the anodically stable SL reduces HF generation and effectively mitigates TM dissolution, SL containing electrolytes are demonstrated to be less capable of supporting Li-ion transport and thus show lower cycling stability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...