A municipal wastewater treatment plant “drinking beer” for reduction of cost and carbon emission
Abstract
In wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs), external carbon sources are often required due to low C/N influent. However, the use of external carbon sources can increase treatment costs and cause large carbon emissions. Beer wastewater, which contains a substantial amount of carbon, is often treated separately in China, consuming significant energy and cost. However, most studies using beer wastewater as an external carbon source are still on a laboratory scale. To address this issue, this study proposes using beer wastewater as an external carbon source in an actual WWTP to reduce operating costs and carbon emissions while achieving a win–win situation. The denitrification rate of beer wastewater was found to be higher 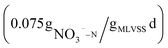 than that of sodium acetate
than that of sodium acetate 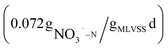 , resulting in improved treatment efficiency of the WWTP. Specifically, COD, BOD5, TN, NH4+–N and TP increased by 3.4%, 1.6%, 10.8%, 1.1%, and 1.7%, respectively. Additionally, the treatment cost and carbon emission per 10 000 tons of wastewater treated were reduced by 537.31 yuan and 2.27 t CO2, respectively. These results indicate that beer wastewater has significant utilization potential and provide a reference for using different types of production wastewater in WWTPs. This study's findings demonstrate the feasibility of implementing this approach in an actual WWTP setting.
, resulting in improved treatment efficiency of the WWTP. Specifically, COD, BOD5, TN, NH4+–N and TP increased by 3.4%, 1.6%, 10.8%, 1.1%, and 1.7%, respectively. Additionally, the treatment cost and carbon emission per 10 000 tons of wastewater treated were reduced by 537.31 yuan and 2.27 t CO2, respectively. These results indicate that beer wastewater has significant utilization potential and provide a reference for using different types of production wastewater in WWTPs. This study's findings demonstrate the feasibility of implementing this approach in an actual WWTP setting.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...