Utilizing modified cellulose nanoparticles derived from a plant loofah sponge to improve the removal of diazinon insecticide from an aqueous medium
Abstract
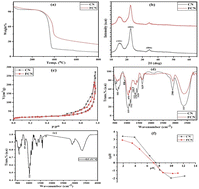
Organophosphate insecticides, such as diazinon, have been well investigated to pose health and environmental risks. In this study, ferric-modified nanocellulose composite (FCN) and nanocellulose particles (CN) based on a natural source as a loofah sponge were synthesized to verify their adsorption potential to eliminate diazinon (DZ) from contaminated water. The as-prepared adsorbents were characterized by performing TGA, XRD, FTIR spectroscopy, SEM, TEM, pHPZC, and BET analyses, in which FCN showed high thermal stability, surface area of 82.65 m2 g−1, surface with mesopores, good crystallinity (61.6%), and particle size of 86.0 nm. The results of adsorption tests demonstrated that the maximum Langmuir adsorption capacity (294.98 mg g−1) was exhibited by FCN at 38 °C, pH 7, 1.0 g L−1 of adsorbent dosage, and 20 h of contact shaking time. The effect of adding KCl solution with high ionic strength (1.0 mol L−1) reduced the DZ removal percent by 52.9%. The experimental adsorption data achieved the best fit with all the applied isotherm models with favorable, physical, and endothermic nature of adsorption consistent with thermodynamic data. Pentanol attained higher desorption efficiency (95%) and was used in five adsorption/desorption cycles in which FCN exhibited only an 8.8% decrease in the removal percent of DZ.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...