Comparison of the pharmacokinetics of timosaponin AIII, timosaponin BIII, and mangiferin extracted from crude and salt-processed Anemarrhenae Rhizoma by UPLC-MS/MS
Abstract
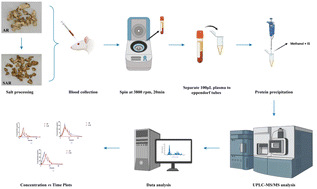
Processing is a traditional method for preparing decoctions of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) that is imperative for reducing toxicity, increasing efficacy, and adjusting the properties of pharmacologically active components of the TCM. Salt processing of Anemarrhenae Rhizoma (AR), a traditional Chinese herb, has been employed since the Song dynasty and can enhance the ability of AR to enriching the Yin and downbearing fire according to the traditional theory recorded in the Enlightenment on Materia Medica. Previous research found that the hypoglycemic effect of AR was enhanced after salt processing, and the concentrations of three components, namely timosaponin AIII, timosaponin BIII, and mangiferin, all of which have hypoglycemic activities, have been found to be significantly increased after salt processing. In this study, we established an ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) method to ultimately measure the concentrations of timosaponin AIII, timosaponin BIII, and mangiferin in rat plasma after administration of unprocessed AR and salt-processed AR (SAR) to the rats to further elucidate how salt processing affects the pharmacokinetic profiles of each of these compounds. Separation was achieved on an Acquity UPLC HSS T3 column. The 0.1% formic acid aqueous solution (v/v) and acetonitrile were used as the mobile phase system. Calibration curves of each compound in blank rat plasma, as well as the accuracy, precision, stability, and recovery of the total three analytes, were then measured to validate the method. The Cmax and AUC0–t values of timosaponin BIII and mangiferin in the SAR group were significantly higher than those of the AR group, while the Tmax values of timosaponin BIII and mangiferin in the SAR group were shorter than in the AR group. These results indicated that salt processing improved the absorption and bioavailability of timosaponin BIII and mangiferin in Anemarrhenae Rhizoma, and they provide a rationale for how the salt processing enhances the hypoglycemic effect of Anemarrhenae Rhizoma.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...