Investigation on the properties and structures of resveratrol-derived epoxy thermosets cured with an active ester†
Abstract
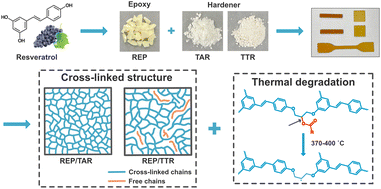
Using biomass resources to prepare thermosets seems to have become a trend in the future of a sustainable society, and an active ester may be an excellent epoxy hardener for the electronic packaging field. In this work, we synthesized a resveratrol-derived epoxy (REP) and two resveratrol-derived active ester hardeners (triacetyl resveratrol (TAR), tri(m-toluoyl) resveratrol (TTR)), and then two resveratrol-derived bio-based epoxy thermosets (REP/TAR, REP/TTR) were prepared by the curing reaction of the epoxy and the hardener. The properties and structures of the thermosets were characterized and investigated. Results showed that the properties of REP/TAR in all aspects were better than those of REP/TTR; to be specific, the REP/TAR exhibited a higher gel fraction and better solvent resistance, indicating its better cross-linked network; the glass transition temperature of REP/TAR was higher and reached 177 °C (DMA) and the thermal stability of TEP/TAR was also better and the char yield at 600 °C was 46.5%. The main reason could be that the steric hindrance of acetyl groups in REP/TAR was smaller than that of m-toluoyl groups in REP/TTR. What's more, a novel analytical method was proposed for use in thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) to analyze the degradation process of thermosets, revealing a degradation process that was unique to the active ester cured epoxy thermosets. In all, the resveratrol-derived biobased epoxy thermosets could be a promising candidate for replacing fossil-derived thermosets and have potential application in the electronic packaging field, and the study on active ester hardeners might inspire the design and synthesis of subsequent active ester hardeners.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...