Factors influencing on-resin depsipeptide bond formation: case studies on daptomycin- and brevicidine-derived sequences†
Abstract
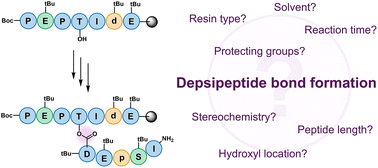
Depsipeptides are an important class of bioactive natural products, where a growing number of genome-mined structures that display anti-microbial activity are macrocyclic depsipeptides. Chemically, peptide ester (depsipeptide) bond formation often displays low yields, and thereby hampers efforts to access these structures for structure–activity studies. Herein, we present a systematic study of the variables that influence depsipeptide bond formation on-resin, using simplified sequences derived from antibiotic peptides, daptomycin and brevicidine, prepared via Fmoc-based solid-phase synthesis. Our study highlights reaction solvent as the key determinant, where switching the solvent from DMF to DCM in almost all cases increased the amount of depsipeptide product. Limiting the number of amino-acids N-terminal to the reactive alcohol was also noted to significantly improve the acylation efficiency. The impact of different N-terminal and side-chain protecting groups, as well as stereochemistry, was also investigated. Additives to the reaction, such as inclusion of surfactants for esterification of long hydrophobic sequences, did not improve conversion. 6-ClHOBt, often added to improve acylation efficiency, notably decreased the amount of depsipeptide observed. Lastly, no significant difference between polystyrene and Tentagel® (PEG-decorated) resins were found for these sequences.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...