Persistent azulene α-carbocations: synthesis from aldehydes, spectroscopic and crystallographic properties†
Abstract
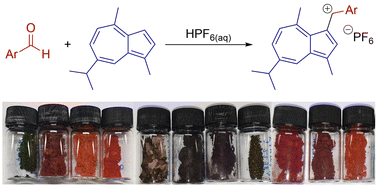
The non-benzenoid aromatic system azulene is sufficiently nucleophilic at C1 that it can react with a protonated aldehyde to form an α-azulenyl alcohol. This in turn may be protonated and undergo loss of water to give an azulene α-carbocation. We report the isolation of such azulenyl cations as salts with non-coordinating anions. The salts have been characterised by NMR, UV/Vis absorption and (in certain cases) X-ray crystallography. Reduction of representative salts to afford azulenyl(aryl) methylenes has been demonstrated.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...