Tuneable-by-design copper oxide nanoparticles in ionic liquid nanofluids†
Abstract
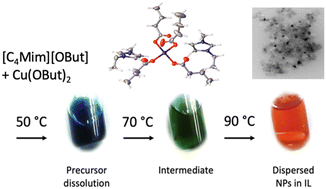
In this study, copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO-NPs) were synthesised in an ionic liquid, [C2MIm][CnHnCO2], and the respective copper(II) carboxylate precursors. Heating the solution to 120 °C caused a colour change from blue to red, indicating a change in copper salt coordination and nanoparticle formation. Crystallography and UV-Vis spectroscopy were used to monitor the transition upon temperature changes. The particle formation was characterised using TEM and SWAXS analyses. The results showed that different anion chain lengths led to different particle sizes. When using copper(II) acetate precursors, the transformation resulted in CuO(I,II) clusters (<1 nm), depending on the imidazolium-based cation used. However, using a copper(II) octanoate precursor, small CuO-NPs in the range of 10–25 nm were formed, while larger CuO-NPs were obtained using a copper(II) butanoate precursor in the range of 10–61 nm.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...