Facile engineering of resveratrol nanoparticles loaded with 20(S)-protopanaxadiol for the treatment of periodontitis by regulating the macrophage phenotype†
Abstract
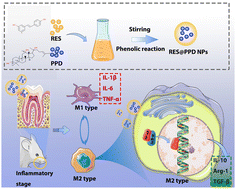
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease, mainly caused by the formation of a subgingival plaque biofilm. In recent years, growing attention has been paid to immunotherapy in the treatment of periodontitis, and the importance of communal intervention associated with macrophage polarization was emphasized. Herein, resveratrol (RES) and 20(S)-protopanaxadiol (PPD) were successfully self-assembled into RES@PPD nanoparticles (NPs) by the phenolic resin reaction. RES@PPD NPs have good stability and biocompatibility. The combined application of PPD and RES enhances the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of nanocomposites, remarkably reduces the level of reactive oxygen species, and finally realizes the coordinated regulation of host immunity in periodontitis. The detailed mechanism is as follows: RES@PPD NPs inhibit M1 polarization of macrophages, promote M2 polarization by scavenging ROS, and then inhibit the NF-κB signalling pathway to regulate host immunity. In the animal model of periodontitis, RES@PPD NPs can remarkably decrease the level of pro-inflammatory cytokines, up-regulate the anti-inflammatory cytokines, and exhibit a profound therapeutic effect on local inflammation. Therefore, RES@PPD NPs are effective in antioxidation and anti-inflammation, thus providing a promising candidate drug for the treatment of periodontitis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...