Investigations on a mononuclear Cu(ii) Schiff base complex: theoretical calculations, catechol oxidase activity, and protein binding interaction analysis†
Abstract
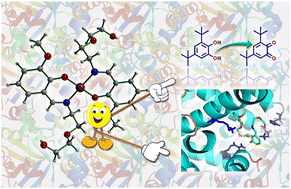
A new mononuclear copper(II) complex [Cu(HL)2](1), has been synthesized from a Schiff base ligand (H2L) and characterized by FTIR spectroscopy, UV-vis spectroscopy, single crystal X-ray diffraction, and powder X-ray diffraction. Single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis established the perfect square planar geometry around the Cu(II) ion (τ4 ≈ 0), obtained by the coordination of the two N and two O atoms from the two deprotonated H2L ligands. However, the electronic spectra of complex 1 displayed a d–d transition band at 959 nm (ε = 73.5 L mol−1 cm−1) in MeCN (10−3 M) suggesting a moderate distortion towards tetrahedral geometry in solution. The DFT-optimized structure of complex 1 in MeCN solvent further supported the distortion of square-planar complex 1 with τ4 ≈ 0.286. Complete active space self-consistent field (CASSCF) calculations in MeCN also suggested a peak at 991 nm (dxy → dx2−y2). which is a very good match with the experimental result. The existence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding interactions (O–H⋯O, 2.012(13) Å) was supported by Hirshfeld surface analysis. Complex 1 was screened for its potential application as a catalyst for the catalytic oxidation of 3,5-di-tert-butyl-catechol (3,5-DTBCH2) and the turnover number (kcat) was found to be 19.87 h−1 in MeCN. We further explored the protein binding interaction ability of complex 1 with bovine serum albumin (BSA) protein using a UV-Vis absorption study and the binding constant (Kb) was determined to be 7.15 × 103 M−1. Additionally, simulation analysis was performed on BSA and human serum albumin (HSA) proteins with complex 1 to gain a more detailed perception of binding interactions at the atomistic level. The simulation study indicated that complex 1 interacted more strongly with BSA with a total of 7 polar interactions than with HSA, which has 6 polar interactions. The most stable interaction with BSA had an energy minimum of −8.6 kcal mole−1 with “0” RMSD.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...