Construction of a S-scheme CdS/CuFe2O4 heterojunction with suppressed charge recombination for enhanced visible light-driven photocatalytic activity†
Abstract
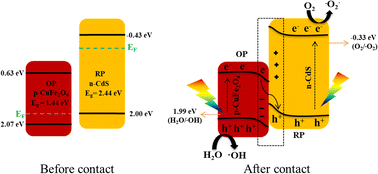
Effective interfacial engineering to fabricate a suitable nano-photocatalyst for environmental remediation is on high demand. A magnetic nanocomposite is a potential candidate for reusability and recovery from treated wastewater. CuFe2O4/CdS nanoclusters (NCs) were fabricated using a chemical co-precipitation method. SEM and TEM images of the fabricated NCs revealed coral-like agglomerations and polycrystalline nature of NCs with clear lattice fringes. XPS and EDAX were performed for elemental analysis. The apparent photodegradation rate of dye by NCs is two-fold higher compared to that of pure CdS and CuFe2O4. The S-scheme interface retained both strong potential e−/h+ for ˙OH and ˙O2− production under visible light illumination. A 97.71% photocatalytic efficiency was retained after six cycles of reuse. This enhancement in the photocatalytic performance of NCs demonstrates their excellent potential to behave as environmental remediating agents.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...