A rapid synthesis of molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for the extraction of performance enhancing drugs (PIEDs)†
Abstract
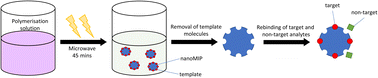
It is becoming increasingly more significant to detect and separate hormones from water sources, with the development of synthetic recognition materials becoming an emerging field. The delicate nature of biological recognition materials such as the antibodies means the generation of robust viable synthetic alternatives has become a necessity. Molecularly imprinted nanoparticles (NanoMIPs) are an exciting class that has shown promise due the generation of high-affinity and specific materials. While nanoMIPs offer high affinity, robustness and reusability, their production can be tricky and laborious. Here we have developed a simple and rapid microwaveable suspension polymerisation technique to produce nanoMIPs for two related classes of drug targets, Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators (SARMs) and steroids. These nanoMIPs were produced using one-pot microwave synthesis with methacrylic acid (MAA) as the functional monomer and ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) as a suitable cross-linker, producing particles of an approximate range of 120–140 nm. With the SARMs-based nanoMIPs being able to rebind 94.08 and 94.46% of their target molecules (andarine, and RAD-140, respectively), while the steroidal-based nanoMIPs were able to rebind 96.62 and 96.80% of their target molecules (estradiol and testosterone, respectively). The affinity of nanoMIPs were investigated using Scatchard analysis, with Ka values of 6.60 × 106, 1.51 × 107, 1.04 × 107 and 1.51 × 107 M−1, for the binding of andarine, RAD-140, estradiol and testosterone, respectively. While the non-imprinted control polymer (NIP) shows a decrease in affinity with Ka values of 3.40 × 104, 1.01 × 104, 1.83 × 104, and 4.00 × 104 M−1, respectively. The nanoMIPs also demonstrated good selectivity and specificity of binding the targets from a complex matrix of river water, showing these functional materials offer multiple uses for trace compound analysis and/or sample clean-up.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...