Reversing silicon carbide into 1D silicon nanowires and graphene-like structures using a dynamic magnetic flux template†
Abstract
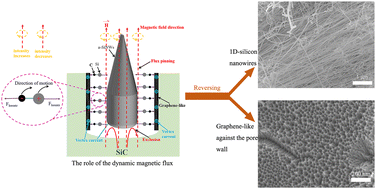
A dynamic magnetic flux template (DMT) method was developed to reverse silicon carbide (SiC) into amorphous silicon nanowires (a-SiNWs) and graphene-like structures driven by both heating and a dynamic magnetic field. The DMT served as a growth template for silicon nanowires, exhibiting an elongated life-time as an anode in a Li-ion battery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...