Naphthyl bearing 1,3,4-thiadiazoleacetamides targeting the parasitic folate pathway as anti-infectious agents: in silico, synthesis, and biological approach†
Abstract
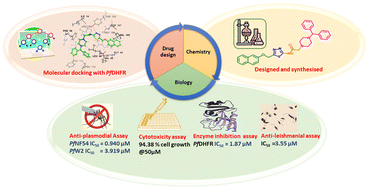
Malaria is still a complex and lethal parasitic infectious disease, despite the availability of effective antimalarial drugs. Resistance of malaria parasites to current treatments necessitates new antimalarials targeting P. falciparum proteins. The present study reported the design and synthesis of a series of a 2-(4-substituted piperazin-1-yl)-N-(5-((naphthalen-2-yloxy)methyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)acetamide hybrids for the inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase (PfDHFR) using computational biology tools followed by chemical synthesis, structural characterization, and functional analysis. The synthesized compounds were evaluated for their in vitro antimalarial activity against CQ-sensitive PfNF54 and CQ-resistant PfW2 strain. Compounds T5 and T6 are the most active compounds having anti-plasmodial activity against PfNF54 with IC50 values of 0.94 and 3.46 μM respectively. Compound T8 is the most active against the PfW2 strain having an IC50 of 3.91 μM. Further, these active hybrids (T5, T6, and T8) were also evaluated for enzyme inhibition assay against PfDHFR. All the tested compounds were non-toxic against the Hek293 cell line with good selectivity indices. Hemolysis assay also showed non-toxicity of these compounds on normal uninfected human RBCs. In silico molecular docking studies were carried out in the binding pocket of both the wild-type and quadruple mutant Pf-DHFR-TS to gain further insights into probable modes of action of active compounds. ADME prediction and physiochemical properties support their drug-likeness. Additionally, they were screened for antileishmanial activity against L. donovani promastigotes to explore broader applications. Thus, this study provides molecular frameworks for developing potent antimalarials and antileishmanial agents.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...