Selectively inhibiting malignant melanoma migration and invasion in an engineered skin model using actin-targeting dinuclear RuII-complexes†
Abstract
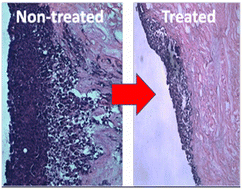
Due to the poor prognosis of metastatic cancers, there is a clinical need for agents with anti-metastatic activity. Here we report on the anti-metastatic effect of a previously reported Ru(II) complex [{(phen)2Ru}2(tpphz)]4+, 14+, that has recently been shown to disrupt actin fiber assembly. In this study, we investigated the anti-migratory effect of +14+ and a close structural analogue+, 24+, on two highly invasive, metastatic human melanoma cell lines. Laser scanning confocal imaging was used to investigate the structure of actin filament and adhesion molecule vinculin and results show disassembly of central actin filaments and focal adhesions. The effect of both compounds on actin filaments was also found to be reversible. As these results revealed that the complexes were cytostatic and produced a significant inhibitory effect on the migration of both melanoma cell lines but not human dermal fibroblasts their effect on 3D-spheroids and a tissue-engineered living skin model were also investigated. These experiments demonstrated that the compounds inhibited the growth and invasiveness of the melanoma-based spheroidal tumor model and both complexes were found to penetrate the epidermis of the skin tissue model and inhibit the invasion of melanoma cells. Taken together, the cytostatic and antimigratory effects of the complexes results in an antimetastatic effect that totally prevent invasion of malignant melanoma into skin tissue.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...