Biobased and degradable thiol–ene networks from levoglucosan for sustainable 3D printing†
Abstract
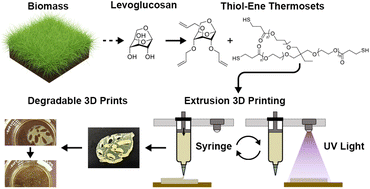
Levoglucosan is a renewable chemical obtained in high yields from pyrolysis of cellulosic biomass, which offers rich functionality for synthetic modification and crosslinking. Here, we report the facile and scalable synthesis of a family of biobased networks from triallyl levoglucosan and multifunctional thiols via UV-initiated thiol–ene click chemistry. The multifunctional thiols utilized in this study can also be sourced from renewable feedstocks, leading to overall high bio-based content of the synthesized levoglucosan networks. The thermomechanical and hydrolytic degradation properties of the resultant networks are tailored based on the type and stoichiometric ratio of thiol crosslinker employed. The Young's modulus and glass transition temperature of levoglucosan-based networks are tunable over the wide ranges of 3.3 MPa to 14.5 MPa and −19.4 °C to 6.9 °C, respectively. The levoglucosan-based thermosets exhibit excellent thermal stability with Td,10% > 305 °C for all networks. The suitability of these resin formulations for extrusion-based 3D printing was illustrated using a UV-assisted direct ink write (DIW) system creating 3D printed parts with excellent fidelity. Hydrolytic degradation of these 3D printed parts via ester hydrolysis demonstrated that levoglucosan-based resins are excellent candidates for sustainable rapid prototyping and mass production applications. Overall, this work displays the utility of levoglucosan as a renewable platform chemical that enables access to tailored thermosets important in applications ranging from 3D printing to biomaterials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...