Sequential chemo–biocatalytic synthesis of aroma compounds†
Abstract
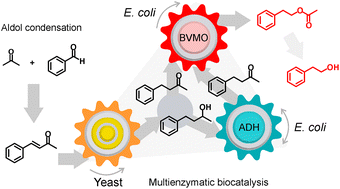
A large number of multienzymatic reactions allow access to chemical compounds with variable structures for diverse applications. One of the most attractive targets is the production of small bioactive compounds, such as aroma and flavour compounds. 2-phenylethyl acetate (2-PEA) and 2-phenylethanol (2-PE) are two rose-like aroma compounds massively used by the industry as fragrance ingredients in cosmetic and non-cosmetic products, as well as flavours and aromas in food and drink preparations. Although there have been several approaches to produce them biotechnologically, the vast majority of these compounds is obtained by chemical synthesis. In this work, we propose a new eco-friendly route towards 2-PEA and eventually 2-PE from simple starting materials. The route involves a solvent-free aldol condensation reaction, followed by a biocatalytic cascade, which involves a Baeyer–Villiger monooxygenase and other redox biocatalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...