The relationship between vitamin K and T2DM: a systematic review and meta-analysis†
Abstract
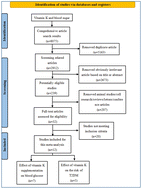
Background: Previous studies have shown the potential role of vitamin K supplementation in the prevention and treatment of many diseases. However, the effect of vitamin K supplementation on blood glucose remains controversial. The purpose of this study was to assess the effects of vitamin K supplementation on glycemia-related indicators, including Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS), Fasting Insulin (FINS) and Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR). The potential association between vitamin K and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) risk was also evaluated. Methods: Up to April 2023, Cochrane, PubMed, Web of Science, Medline and EMBASE databases were searched to assess the effects of vitamin K on blood glucose and the risk of developing T2DM. Results: A meta-analysis of seven studies (813 participants) found vitamin K supplementation significantly reduced FBS (SMD = −0.150 mg dl−1, 95% CI = −0.290, −0.010 mg dl−1) and HOMA-IR (SMD = −0.200, 95% CI = −0.330, −0.060), but not FINS. Five studies with a total of 105 798 participants were included in the meta-analysis of the association between vitamin K and T2DM. The results showed that vitamin K was associated with the reduced risk of developing T2DM (HR = 0.79, 95% CI [0.71–0.88], P < 0.001). Conclusion: The meta-analysis demonstrated that vitamin K supplementation had a significant effect on the regulation of FBS and HOMA-IR in the population. Moreover, vitamin K was associated with the reduced risk of developing T2DM. Considering some limitations found in this study, additional data from large clinical trials are needed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...