Bioavailability of Korean mint (Agastache rugosa) polyphenols in humans and a Caco-2 cell model: a preliminary study exploring the efficacy
Abstract
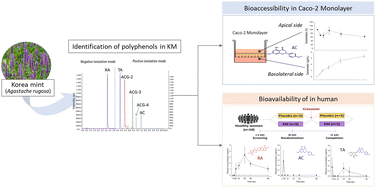
Agastache rugosa, commonly known as Korean mint (KM), is a medicinal plant renowned for its potential health-promoting properties. However, the lack of bioavailability studies has hindered the acquisition of conclusive evidence. In this study, we investigated the bioavailability of six key polyphenols present in KM, including rosmarinic acid (RA), acacetin (AC), and four glycosides of AC. Utilizing UPLC-MS/MS, we analyzed their presence in human plasma and Caco-2 monolayers grown in permeable filter supports. Following single ingestion, we were able to detect RA, AC, and tilianin (TA) in the plasma. Consistent results were obtained for AC and TA but no transport was found for RA in a highly tight Caco-2 cell monolayer, indicating transport through the intercellular space for RA and transepithelial transport for AC and TA. Other AC glucosides with acetyl and/or malonyl groups were rarely found in the plasma. Interestingly, AC glucosides with only an acetyl group appeared at the basolateral side in Caco-2 monolayers, suggesting exclusive hydrolysis of malonyl glucosides in the colon. These findings highlight the high potential of RA, AC, and TA as bioactive compounds that may confer health benefits.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...