Gut microbiome–serum metabolic profiles: insight into the hypoglycemic effect of Porphyra haitanensis glycoprotein on hyperglycemic mice
Abstract
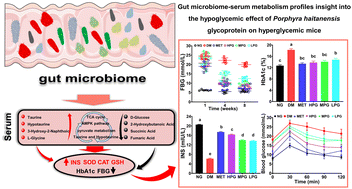
The hypoglycemic activity of natural algal glycoproteins has attracted interest, but studies of their mechanism of regulating glucose metabolism are lacking. This study investigated the hypoglycemic activity of Porphyra haitanensis glycoprotein (PG) in a mouse hyperglycemia model. The underlying mechanism was elucidated by monitoring changes in the gut microbiome and untargeted serum metabolomics. The results indicated that 30–300 mg kg−1 PG regulated blood glucose levels by increasing insulin secretion, reducing glycated hemoglobin, and improving streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemia in a concentration-dependent manner. In particular, 300 mg kg−1 PG decreased fasting blood glucose by 63.11% and glycosylated hemoglobin by 24.50% and increased insulin secretion by 163.97%. The mechanism of the improvement of hyperglycemia by PG may involve regulating beneficial intestinal bacteria (e.g., norank_f__Muribaculaceae and Lachnospiraceae) and altering the serum metabolic profile (e.g., upregulation of hypotaurine, 3-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid, and L-glycine), to regulate taurine and hypotaurine, the TCA cycle, AMPK, and pyruvate metabolism. Our findings supported the development of Porphyra haitanensis and its glycoprotein as novel natural antidiabetic compounds to regulate the glycemic balance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...