An aqueous olive leaf extract (OLE) ameliorates parameters of oxidative stress associated with lipid accumulation and induces lipophagy in human hepatic cells†
Abstract
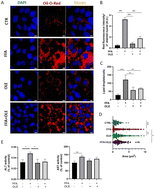
Fatty liver is a disease characterized by a buildup of lipids in the liver, often resulting from excessive consumption of high-fat-containing foods. Fatty liver can degenerate, over time, into more severe forms of liver diseases, especially when oxidative stress occurs. Olive leaf extract (OLE) is a reliable source of polyphenols with antioxidant and hypolipidemic properties that have been successfully used in medicine, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical products. Using “green” solvents with minimal impact on the environment and human health, which simultaneously preserves the extract's beneficial properties, represents one of the major challenges of biomedical research. In the present study, we assayed the potential antioxidant and lipid-lowering effect of a “green” OLE obtained by a water ultrasound-assisted extraction procedure, on the human hepatic HuH7 cell line, treated with a high concentration of free fatty acids (FFA). We found that high FFA concentration induced lipid accumulation and oxidative stress, as measured by increased hydrogen peroxide levels. Moreover, the activity of antioxidant enzymes, catalase, superoxide dismutase, and glutathione peroxidase, was reduced upon FFA treatment. Coincubation of high FFA with OLE reduced lipid and H2O2 accumulation and increased the activity of peroxide-detoxifying enzymes. OLE ameliorated mitochondrial membrane potential, and hepatic parameters by restoring the expression of enzymes involved in insulin signaling and lipid metabolism. Electron microscopy revealed an increased autophagosome formation in both FFA- and FFA + OLE-treated cells. The study of the autophagic pathway indicated OLE's probable role in activating lipophagy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...