Anti-tumor effect of infant-derived Enterococcus via the inhibition of proliferation and inflammation as well as the promotion of apoptosis†
Abstract
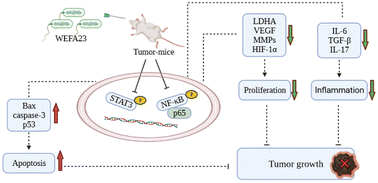
Probiotic Enterococcus hirae WEHI01 and Enterococcus faecium WEFA23 from infants were previously found to effectively inhibit the development of melanoma. In this study, their immunomodulatory and antitumor mechanisms were systemically studied. In vitro assay showed that E. hirae WEHI01 and E. faecium WEFA23 achieved biphasic immune regulation, which was revealed by the activation of resting spleen lymphocytes and RAW264.7 macrophages, as well as the anti-inflammation effect when immune cells were treated with LPS. The antitumor effects of E. hirae WEHI01 and E. faecium WEFA23 in vitro and vivo were then investigated. CCK8 and the cell scratch assay showed that the conditioned media, which were co-incubated with Enterococcus and spleen lymphocytes, significantly inhibited the proliferation and migration of B16F10, HepG-2 and HT-29 cells. The results of the tumor-bearing mice model experiment showed that E. faecium WEFA23 inhibition of the growth of tumors in mice, and the anti-tumor mechanism involved three aspects, namely tumor proliferation (decreasing expressions of LDHA, VEGF, MMP2, MMP9 and HIF-1α), inhibition of the pro-inflammation state (decreasing expressions of IL-6, TGF-β and IL-17) and the promotion of apoptosis (increasing expression of Bax/Bcl-2, caspase-3 and p53). The results suggest that the two strains of Enterococcus could be promising candidates for treating melanoma with a highly inhibitory effect.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...