Perillartine protects against metabolic associated fatty liver in high-fat diet-induced obese mice†
Abstract
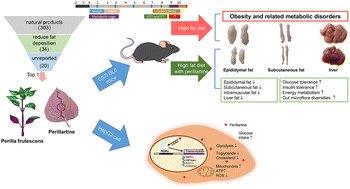
Metabolic associated fatty liver disease is the main cause of chronic liver disease in the world, but there is still no effective treatment. In the search for drugs to treat liver steatosis, we screened 303 natural products using HepG2 cells and discovered that perillartine derived from Perilla frutescens (L.) improved fat deposition as well as glucose homeostasis in hepatocytes. In vitro, perillartine reduced the expression of genes involved in lipid synthesis, lipid transport, and gluconeogenesis in hepatocytes, increased the number of mitochondria, and upregulated the phosphorylation of Akt. In vivo, perillartine reduced body weight gain and the fat rate, improved glucose metabolism and energy balance, and altered the gut microbial composition in mice given a high-fat diet. In addition, RORγ was identified as a possible target of perillartine through pharmacophore screening. Functional studies revealed that the overexpression of RORγ blocked the effects of perillartine, suggesting that it reduced lipid accumulation and regulated glucose metabolism by inhibiting the transcriptional activity of RORγ. Our results provide new information on a natural product inhibitor for RORγ and reveal that perillartine is a new candidate for the treatment of obesity and metabolic associated fatty liver disease.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...