Effects of mixtures of ethanol–calcium chloride–carboxymethylcellulose on the bovine milk whey freeze concentration process†
Abstract
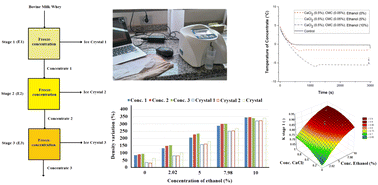
For a long time bovine milk whey (BMW) was considered a residue. However, considering the protein contents, lactose contents and other constituents, BMW has always presented good potential for the manufacture of various by-products of nutritional value. Due to the low temperature, the BMW freeze concentration influences the lactose crystallization, the protein structures and the bioactive compound preservation resulting from water separation as ice crystals. The separation results in increased content and improved functionality of these constituents. The effects of ethanol, calcium chloride (CaCl2) and carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) concentrations on physicochemical properties, rheological parameters and temperature profiles in the freeze concentration (FC) of BMW from cheese enzymatic coagulation were evaluated. The results showed that the effects of ethanol, CaCl2 and CMC addition were significant (p < 0.05) on percentage variations in density, lactose content, total soluble solids and protein content. The number of stages influenced the freeze-concentration process. In the “concentrate” fraction, the largest variations in density, lactose content, SST content and protein content were found in the treatment consisting of 10% ethanol, 0.5% CaCl2 and 0.05% CMC. The results were supported by the analysis of the levels of subcooling and initial freezing temperatures obtained through temperature profiles and in the increase of viscosities of the “concentrated” and “ice crystal” fractions. The use of substances that interfere in the ice crystal formation in the freeze concentration process that precedes the drying process showed remarkable results in the constitution of the final products, used as ingredients in various food formulations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...