Revealing the charge transfer mechanism and assessing product toxicity in the 2D/1D Bi2O2CO3/Bi8(CrO4)O11 heterostructure system†
Abstract
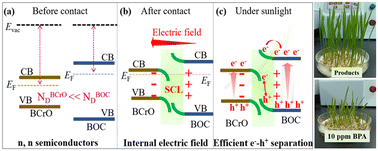
With improved charge separation efficiency, heterojunction catalysts are widely used to enhance photocatalytic activity. However, the transfer mechanism of photoexcited charge carriers remains unclear. In this work, we report for the first time on the use of the type I heterojunction, Bi2O2CO3/Bi8(CrO4)O11, with varying mass ratios for water purification and explore the mechanism of charge transfer. The 20% Bi2O2CO3/Bi8(CrO4)O11 heterojunction showed the highest photocatalytic activities for the degradation of typical dyes and antibiotics, including bisphenol A (BPA), methylene blue (MB), rhodamine B (RhB), methyl orange (MO) and tetracycline (TC). The BPA photodegradation rate was 2.37 and 8.83 times higher than those of Bi8(CrO4)O11 and Bi2O2CO3, respectively. The results demonstrate that the internal electric field between Bi2O2CO3 and Bi8(CrO4)O11 can significantly boost the photocatalytic efficiency through highly promoted separation of electron–hole pairs by forming the S-scheme heterojunction. The trapping experiments and electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) results indicate that hydroxyl radicals, holes and superoxide radicals all act as active species in the Bi2O2CO3/Bi8(CrO4)O11 heterojunction, efficiently extending the practical application of photocatalysts. The possible photodegradation pathways of MB and BPA were proposed based on the results of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). Furthermore, we verified that BPA solutions treated with Bi2O2CO3/Bi8(CrO4)O11 heterojunctions are harmless for wheat seed germination. The 2D/1D Bi2O2CO3/Bi8(CrO4)O11 photocatalysts displayed great potential as an environmentally friendly strategy for wastewater purification.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...