Limitations of conventional approaches to identify photochemically produced reactive intermediates involved in contaminant indirect photodegradation†
Abstract
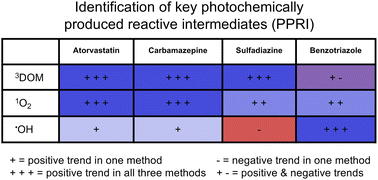
Dissolved organic matter (DOM) mediated indirect photodegradation can play an important role in the degradation of aquatic contaminants. Predicting the rate of this process requires knowledge of the photochemically produced reactive intermediates (PPRI) that react with the compound of interest, as well as the ability of individual DOM samples to produce PPRI. Key PPRI are typically identified using quencher studies, yet this approach often leads to results that are difficult to interpret. In this work, we analyze the indirect photodegradation of atorvastatin, carbamazepine, sulfadiazine, and benzotriazole using a diverse set of 48 waters from natural and engineered aquatic systems. We use this large data set to evaluate relationships between PPRI formation and indirect photodegradation rate constants, which are directly compared to results using standard quenching experiments. These data demonstrate that triplet state DOM (3DOM) and singlet oxygen (1O2) are critical PPRI for atorvastatin, carbamazepine, and sulfadiazine, while hydroxyl radical (˙OH) contributes to the indirect photodegradation of benzotriazole. We caution against relying on quenching studies because quenching of 3DOM limits the formation of 1O2 and all studied quenchers react with ˙OH. Furthermore, we show that DOM composition directly influences indirect photodegradation and that low molecular weight, microbial-like DOM is positively correlated with the indirect photodegradation rates of carbamazepine, sulfadiazine, and benzotriazole.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Contaminant remediation and fate


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...