Occurrence and removal of four artificial sweeteners in wastewater treatment plants of China†
Abstract
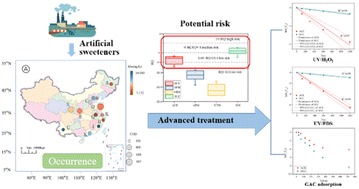
Artificial sweeteners discharged into aquatic environments have raised concern because of their ubiquitous occurrence and potential biological effect. And some of them, such as sucralose (SUC) and acesulfame (ACE), have been identified as emerging contaminants. Wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) are considered as important sources and sinks of artificial sweeteners discharged into the environment. In this study, the occurrence and removal of four representative artificial sweeteners in 12 WWTPs located in different provinces of China were investigated. The results showed that artificial sweeteners were detected widely in the investigated WWTPs. The median concentrations of the four target artificial sweeteners were detected in influents at levels of 0.03–3.85 μg L−1 and decreased in the order of SUC > ACE > aspartame (APM) > neotame (NTM). Additionally, the per capita mass loads of total artificial sweeteners in the WWTPs could be affected by the location of the WWTPs and were higher in southern cities than in northern cities. It was also found that there was a distinct linear correlation between the per capita mass load of ACE in influents and population density. During the treatment of WWTPs, the overall removal efficiency of artificial sweeteners ranged from −116% to 99.1%. Among the target artificial sweeteners, SUC and ACE might have potential risk to aquatic environments based on the calculation of the risk quotient. Thus, advanced treatment processes were carried to further remove SUC and ACE to reduce their long-term cumulative effect. Overall, UV/H2O2 and UV/PDS showed a better effect than granular activated carbon (GAC) adsorption in the removal of artificial sweeteners. The reaction constants of ACE by UV/H2O2 and UV/PDS were higher than those of SUC, which is related to molar extinction coefficients. Meanwhile, the adsorption ability of GAC adsorption for SUC was better than that of ACE, which is in correlation with the octanol–water partition coefficient. By comparison of removal efficiency, UV/PDS was considered as the most suitable advanced treatment process to remove ACE and SUC.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Contaminant remediation and fate


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...