Unraveling the temperature-responsive solvation structure and interfacial chemistry for graphite anodes†
Abstract
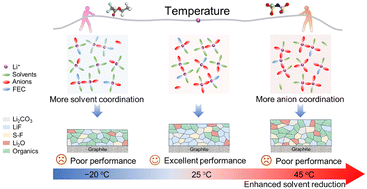
The variation of temperature induces a corresponding transformation of the primary solvation structure of Li+ due to the competition coordination of solvents and anions with Li+. However, the specific variations and their effect on the interfacial chemistry are less-studied and ambiguous. Herein, the correlation of the temperature-responsive solvation structure, interfacial chemistry and electrochemical performance of graphite anodes is systematically investigated to figure out the structure–property relationships. Spectra analysis and molecular dynamics simulations reveal that increasing the temperature causes enhanced Li+–anion interaction and weakened Li+–solvent interaction in the primary solvation structure of Li+. This easily generates the anion-dominated solvation sheath and the corresponding inorganic-rich solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) with increasing temperature. However, the projected density-of-states calculations and thermal analysis witness that more solvents tend to be reduced at high temperatures, which results in an obvious increase of organic species in the interphase. Given the synergistic effect of the temperature-responsive solvation structure and thermal reduction, the SEI formed at 25 °C has been equipped as a stable LiF-rich inorganic film with moderate thickness and low energy barrier for smooth Li+ diffusion. These features enable graphite anodes with a super-fast rate capability of 256 mA h g−1 at 5C under 25 °C and high-capacity retention of 50.4% even at −45 °C compared to that at 25 °C. This study reveals the correlation between the temperature-responsive solvation structure and interfacial chemistry, providing a viewpoint on designing temperature-adaptative batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...