Preparation, thermal storage properties and application of sodium acetate trihydrate/expanded graphite composite phase change materials
Abstract
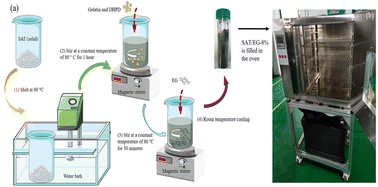
The development of energy storage technology is beneficial for the efficient use of energy and sustainable development. As an effectual approach for storing and transporting thermal energy, latent heat storage using phase change materials (PCMs) has attracted tremendous attention. However, low thermal conductivity, poor stability, and leakages are considerable challenges to the widespread application of solid–liquid PCMs. Composite phase change materials (CPCMs) were prepared by combining expanded graphite (EG) and sodium acetate trihydrate (CH3COONa·3H2O, SAT). EG as a supporting material plays a crucial part in both enhancing the thermal conductivity and preventing the melted PCMs from leakage. The chemical structure, micromorphology, thermal stability, thermal conductivity, phase change behavior and heat storage performance of SAT/EG CPCMs have been extensively investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), thermal conductivity analysis, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and cycling stability measurement. The results of SEM indicate that EG with a loose and porous layered structure has a good molding effect and can adsorb SAT well. XRD and FTIR results show that only a simple physical combination between EG and SAT exists, and no new substances have been produced. Compared with pure SAT, thermal conductivity and supercooling tests show that the supercooling degree of the CPCMs was decreased and the thermal conductivity was increased by 205.1%. In addition, the addition of 2 wt% of disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate (Na2HPO4·12H2O, DHPD) as a nucleating agent and 0.5 wt% of gelatin as a thickening agent to SAT could reduce the supercooling degree and inhibit the phase separation well. Based on SAT/EG-8% CPCMs, an oven with phase change energy storage was designed and the heat storage/release performance of the oven was investigated under different operating conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...