Anion-directed structural tuning of two azomethine-derived Zn2+ complexes with optoelectronic recognition of Cu2+ in aqueous medium with anti-cancer activities: from micromolar to femtomolar sensitivity with DFT revelation†
Abstract
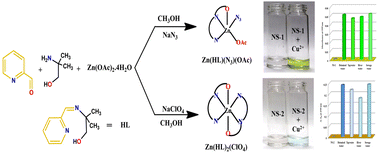
Herein, two novel mononuclear transition metal Zn2+ complexes i.e. [Zn(HL)(N3)(OAc)] (NS-1) & [Zn(HL)2(ClO4)2] (NS-2) have been synthesised using a tridentate clickable Schiff base ligand, HL (2-methyl-2-((pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino)propan-1-ol), and the polyatomic monoanions N3− and ClO4− for NS-1 and NS-2 respectively. Interestingly, NS-1 and NS-2 have been explored for the detection of Cu2+ with an LOD of 48.6 fM (response time ∼6 s) and 2.4 μM respectively through two mutually independent pathways that were studied using sophisticated methods like UV-Vis, cyclic voltammetry, ESI-MS etc. with theoretical DFT support. Herein, both chemosensors are equally responsive towards the detection of Cu2+ in aqueous as well as other targeted real field samples with appreciable recovery percentage (74.8–102%), demonstrating their practical applicability. Moreover, the detection of unbound Cu2+ in a human urine specimen was also analysed which may be helpful for the diagnosis of Cu2+-related disorders like Wilson's disease. Taking one step ahead, TLC strips have been employed for on-field detection of the targeted analytes by contact mode analysis. Additionally, the anti-cancer activity of these complexes has also been studied on breast cancer cells with the help of the MTT assay. It has been found that at a 0.5 mM dose, both NS-1 and NS-2 could kill 81.4% and 73.2% of cancer cells respectively. However, it has been found that NS-1 destroys normal cells together with cancer cells. Hence, NS-2 could be administered as a better anticancer drug for MDA-MB-231 cancer cells in comparison with NS-1. In a nutshell, the present work describes how anion-directed synthesis of two architecturally different metal complexes leads toward the detection of the same analyte via an independent chemodosimetric pathway along with their anti-cancer activities on breast cancer cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...